What is a startup?
A startup is a young company with a business model that supports innovation. For example, if you were to develop a unique software program that addresses an unsolved widespread problem, create a business plan, and acquire funding, you’d be a tech startup entrepreneur!
Startup companies, unlike large bulky corporations, are lean in their operations and focus on rapid growth in the very beginning.
In this article, we’ll further explain what defines a startup company, how startups are typically funded, and more.
Ready to launch a company? Check out our list of startup ideas and our guide on how to start a startup.
nullIs a Startup Company?
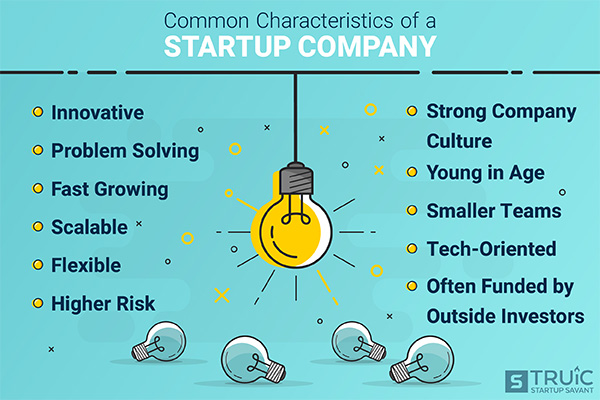
As the term implies, ‘startup’ is not a permanent phase for any business — nor does it solely refer to companies in the tech sphere. It’s a vital, early stage of the business life cycle, and can refer to virtually any industry.
In general, startups tend to have few employees and fast growth potential. They provide products with widespread appeal that either don’t exist yet, or solve a problem better than the options currently available.
Here are the main characteristics of a startup company:
- Innovative
- Disruptive
- Problem solving
- Fast growing
- Scalable
A Brief History of Startups
Startups haven’t always been viewed in a positive light. Many people blame the events of the Great Depression for reckless startup investing, which led to legislation restricting the way unregulated companies could advertise for investors. Since then, startup funding has largely been provided through venture capital firms or “friends and family” investors.
The modern-day popularity of startups has its roots in the dot-com boom of the late 1990s. Investing in small-scale businesses was extremely commonplace during the rise of the internet — which is also the reason many people associate startups with tech firms to this day.
Startup Facts
- A startup company is designed to grow rapidly and scale upward without geographical constraints. This is the primary differentiator between startups and other young businesses.
- Most startups’ expenses exceed their revenue, which is why so many of them require external financing. Without it, there would be no way for these companies to effectively develop and market their innovative products or services.
- Oftentimes startups are built around an exit strategy — they’re designed with the end goal of selling the company to a larger corporation.
- Many startup owners are “serial entrepreneurs.” They’ll come up with a startup’s initial idea, put in the work to get the ball rolling, then hand off the day-to-day responsibilities to someone else so they can focus on launching one of their other startup projects.
Learn more about the anatomy of an entrepreneur and visit our startup founder series to gain entrepreneurship insights, lessons, and advice from founders themselves.
Examples of Startups
Some of the most innovative products and services you use today were likely the result of a startup that succeeded and made its way into the broader marketplace. We’re going to walk through some examples of innovative startups, and how they were able to reach millions of customers and make a positive impact in the world.
Facebook began as a small startup company that was intended to be a social network for students on college campuses. Over time, they continued to grow, develop their platform, and are now used by billions of people all over the world to stay in touch with loved ones.
Mailchimp
Mailchimp began as a small startup but has grown into one of the largest email providers in the world. Small businesses everywhere are in need of reliable email providers who have high deliverability and can ensure their messages get to their prospects or customers without being lost in transit or sent to spam. Mailchimp was able to create a platform that’s easy to use and enjoyable.
Airbnb
The hospitality industry was completely transformed by Airbnb. Instead of staying in and booking hotels, travelers could now rent out someone’s home and enjoy the benefits of staying in a cozy, homely space. Airbnb has now grown worldwide and is used by travelers for lodging and hosts as a source of income.
Types of Startups
Getting to know the type of startup company you want to create will help you establish the market and growth potential available to you. There are six types of startups, all best suited for a different type of entrepreneur based on their abilities, goals, and wants.
Lifestyle Startups
Lifestyle startups are companies that are centered around the founder’s interests and passions. This kind of startup business allows the founder(s) to participate in their favorite activities, and hopefully make money doing so. For example, a passionate guitarist that opens a music store or starts a business teaching music lessons; this would be considered a lifestyle startup.
Small Business Startups
A small business startup isn’t usually created with scalability in mind. These startup companies are born out of a desire to start a small business that will provide enough capital to be financially stable but not necessarily to grow tremendously. An example of a small business startup could be a small grocery store, salon, or restaurant.
Scalable Startups
A scalable startup is a growth-oriented company that takes an idea or concept and works to rapidly grow the new business and achieve the highest profit as quickly possible (think Silicon Valley or New York startups). This type of startup requires thorough market research to identify exploitable market opportunities.
Social Startups
Social entrepreneurship startups are created to make a difference or positive impact on the world around them. Unlike other types of startups, social entrepreneurship startups are not created to gain wealth; though it is possible to profit from this type of startup business model unless it is a nonprofit organization. They are created with the intention of using an idea to create positive change.
Large Company Startups
Growing a big business takes innovation and reimagining; this is how (and why) large company startups are born. Startups that are created by large companies in order to introduce a new product, or to reach a new audience, are backed by the support and capital of the big business. Any new business created by a large, existing company would be considered a large company startup.
Buyable Startups
Buyable startups are companies that are built with the intention of being acquired or bought in the future. Rather than grow or expand their new business, these startups are created with the hopes of being acquired early on.
Need some inspiration to help you launch your company? Check out our list of the top startups to watch!
Startup Funding
As mentioned previously, startups are typically funded by the startup owner’s friends and family, or by venture capital firms. These firms, which gained popularity in the 1970s, provide seed money from a group of investors and mitigate risk by pooling together venture capital funds to invest in a variety of startups.
Continue reading to learn more about the various ways startups raise capital.
Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping means to build your startup company with no outside financing. Essentially, you invest your own savings; utilizing the resources you already have to build your business from the ground up. Once your self-started business is established, your initial profits are then invested back into your business until you receive additional capital or your business grows substantially.
Friends and Family
Most startups rely on friends and family loans to get their business off the ground. Sourcing funding from close relationships isn’t typically as simple as asking the question over coffee; asking friends and family to invest in your business should be done with care. Four steps to respectfully source financing from friends and family: Present your case, propose clear repayment terms, share your backup plan, then create a written agreement.
Crowdfunding
The rise of crowdfunding has largely revolutionized the way startups are funded. Crowdfunding allows people from around the world to invest in companies using a tiered reward system that provides equity in return. Some niche crowdfunding sites are aimed solely toward startup funding, but even mainstream crowdsourcing platforms like Indiegogo offer equity-based financing opportunities. Some niche crowdfunding sites are aimed solely toward startup funding such as SeedInvest and CircleUp, but even mainstream crowdsourcing platforms like Indiegogo and WeFunder offer equity-based funding opportunities.
Venture Capital (VC) Firms
VC firms invest in startups to gain profit as the company grows through funding phases such as Series A, B, C, and D. They typically will take an active role in the business, sit on the board of directors, or request to become part owner of the startup. Since VC investments are done in exchange for equity rather than debt, your startup company will need to show promise of high-growth potential and innovation in order to secure this type of funding.
Angel Investors
Similar to VC firms, an angel investor provides capital for startups in hopes of a high return on investment (ROI). Typically, angel investors (also known as business angels) are people with an excess of money to spend on risky investments. Many times these investors provide seed funding during the early stages of a startup that can be difficult to secure financing for.
Startup Accelerator
Startup accelerators are programs that offer funding and resources such as mentorship to startups in their early stages. Once used by successful startups such as AirBnB and PillPack, these are fixed-term programs built to supply aspiring entrepreneurs with the information, community, and capital needed to create the startup of their dreams.
Startup Incubator
Startup incubators are community-based programs for entrepreneurs in the early stages of their startup’s lifespan that provide initial funding, mentorship, and training. Typically, startup incubators are housed in a collaborative space that encourages community building with a month-to-month lease that gives entrepreneurs access to a shared space and all the tools their program has to offer.
Startup Grants
Unlike loans, startup grants provide capital for entrepreneurs that you don’t have to pay back. Most often startup grants are given either by the government or organization to startups that apply and meet the qualifications of the grant. Many startup grants are given with specific rules and regulations that dictate the way the money is spent; for example, if a grant is given to your startup to invest in developing new technology, it cannot be used for any other purpose.
Startup Loans
Startup loans are funding that is paid back to the lender. These loans can be acquired by applying with a business lender such as a bank or another lending institution. However, there are requirements that you’ll need to fulfill in order to receive this type of financing such as creating a business plan and the proper documentation required by the lender. We recommend checking out our guide on how to get a startup business loan.
Startup Investing
The most common types of startup investors are venture capitalists (VCs) and angel investors, also known as “angels.” As a startup founder seeking investment, you’ll want to determine what percentage of your business you’re willing to give up for an investment in your company.
Typically, investors can request anywhere from 20%-25% of your business in return for capital investment. You should be prepared to negotiate with investors and understand the amount of capital you require to get your startup off the ground.
Many startups also choose to receive funding through a startup accelerator, such as Y Combinator. Accelerator programs provide investment opportunities for startups and give them the resources they need to succeed.
Pros and Cons of Startups
Starting your own business is no easy task, and it often requires long hours, perseverance, and a constant drive to hit your goals and make your vision a reality. Here are some of the pros and cons of startups, and what you could expect as a founder.
Advantages
Creating your own startup company has a large number of advantages, and founders often see the pros as outweighing the potential cons. As a founder, you’ll have the ultimate form of flexibility in how you run your business, the decisions you make, and the projects and opportunities you wish to pursue.
Startup founders often have a vision they’re trying to make a reality, and a series of goals they are attempting to accomplish through their company. Remember, the primary goal of a successful business is to provide a superior product or service that makes people’s lives better or easier in some way. When you see how you’re positively impacting your customers, you’ll feel a sense of accomplishment and pride.
Additionally, if your startup is successful or acquired by a larger company, the monetary advantages can be life-changing.
Disadvantages
The advantages of startups are plentiful, but there are also some common disadvantages that founders should be aware of.
One of the most prevalent disadvantages when it comes to running your own business is the risk of failure. You are never guaranteed to succeed, and whether your startup is successful is entirely up to you as the founder.
You’ll likely encounter a great deal of stress while building your company, and you’ll be required to deal with your competition, create innovation within your industry, and likely seek capital investment into your business.
All of these items are difficult to achieve in practice and will require a significant amount of work and effort with no guarantee of success. Trying and trying without giving up is how resilient startup owners make their dreams a reality.
Comments
Post a Comment